In the world of luxury textiles, two names often stand out: pashmina and cashmere. Both are renowned for their softness, warmth, and timeless appeal. But what sets them apart?
This article aims to shed light on the key differences between pashmina and cashmere. We’ll delve into their origins, characteristics, and the craftsmanship involved in their production.
Understanding these differences is crucial. It can help you make informed decisions when purchasing these high-quality fabrics. Whether you’re a fashion enthusiast, a luxury textile buyer, or simply curious, this guide is for you.
We’ll also explore the care instructions for both pashmina and cashmere. Proper care is essential to maintain their quality and longevity.
But it’s not just about the fabrics themselves. We’ll also touch on the environmental and ethical considerations surrounding their production.
In a market where the term “pashmina” is often used loosely, knowing what to look for can help you avoid counterfeit or low-quality products.
So, are you ready to unravel the intricacies of pashmina and cashmere? Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Basics
When exploring pashmina and cashmere, it’s important to understand the basics. Both are prized for their luxurious feel. However, their roots and uses vary.
Cashmere and pashmina are often confused as being the same. While both originate from goats, they are quite distinct in certain aspects.
Pashmina is, in fact, a variety of cashmere. The main distinction lies in the type of goat and the regions they are sourced from.
Focusing on these fibers’ unique characteristics helps to better appreciate their qualities. Let’s break down the specifics of each.
To simplify:
- Cashmere is more available globally in multiple forms, including sweaters and other wearables.
- Pashmina is revered specifically for shawls and is often considered the more elite option.
This foundational knowledge is essential before delving deeper into fiber differences.
What is Cashmere?
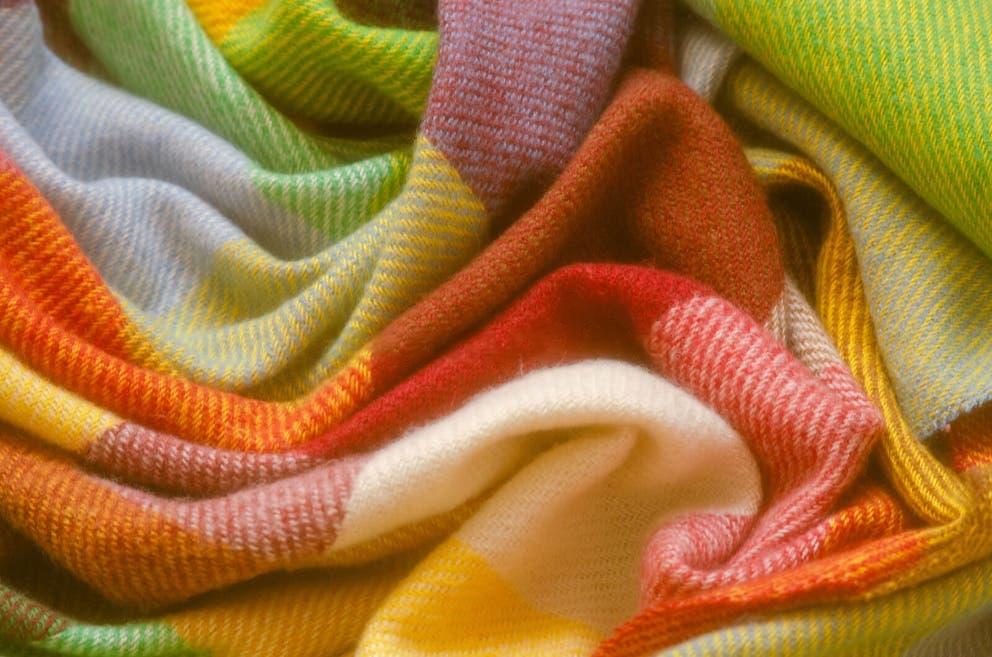

Cashmere is a fiber that exudes elegance and warmth. It is derived from the undercoat of Cashmere goats. These goats are primarily found in Mongolia, China, and Iran.
The fiber is lightweight yet offers remarkable insulation. It has a soft texture that is gentle against the skin, making it a preferred choice for high-end garments.
Cashmere’s appeal is widespread because it provides luxury without bulk. The fiber’s accessibility in various forms contributes to its popularity. From sweaters to scarves, cashmere is a versatile fabric that suits many needs.
What is Pashmina?

Pashmina, often dubbed the “king of fibers,” is a type of cashmere. It is sourced from the rare Changthangi goat. This goat is native to the high-altitude regions of Nepal and the Himalayas.
Pashmina fibers are exceptionally fine, often under 12 microns in diameter. This fineness gives pashmina its renowned softness and delicate touch.
Traditional craftsmanship plays a major role in pashmina’s allure. Hand-spun and hand-woven techniques ensure each piece is unique, adding to its exclusivity. The labor-intensive process and rarity of the raw material often make pashmina products more expensive than regular cashmere.
The Origin and Source of Luxury
Understanding the origins of pashmina and cashmere elevates one’s appreciation for these luxurious fibers. The process begins with their geographic roots, influencing their unique characteristics. The environments where they are sourced play a crucial role in the fibers’ development.
Both pashmina and cashmere fibers originate from goats that have adapted to harsh climates. These animals produce fine undercoats crucial for survival, which we then transform into luxurious fabrics.
The rarity of pashmina largely lies in its geographic specificity. Only certain regions can produce fibers fine enough to meet its standards. Meanwhile, cashmere is more widespread, with broader availability due to its varied origins.
Cultural significance also enhances the fibers’ allure. Pashmina holds deep cultural importance in South Asian regions, often featuring in traditional attire and weddings.
The journey from goat to garment involves meticulous craftsmanship. The dedication of artisans ensures that each piece showcases the highest quality, preserving techniques passed down through generations.
These fibers’ luxurious appeal is deeply rooted in their origins, right from the harsh landscapes to traditional crafting techniques that transform raw fibers into elegant products.
Geographic Origins of Cashmere and Pashmina
Cashmere’s origins span several countries, each contributing to its global presence. Primarily, it comes from Mongolia, China, and Iran, with each region offering fibers of different qualities.
The varying climates in these regions impact the quality of cashmere. They lead to differences in fiber length and softness, affecting the final product’s quality.
In contrast, pashmina is primarily sourced from the Changthangi goats of the Himalayan and Nepalese highlands. These specific geographic conditions produce fibers with exceptional softness and warmth, unmatched by other regions.
The Goats Behind the Fibers
The key to the luxury of pashmina and cashmere lies in their source goats. The Cashmere goat provides fibers that are widely used, known for their fine yet warm qualities. These goats are resilient, thriving in cold climates.
Meanwhile, the Changthangi goat is exclusively responsible for pashmina fibers. These goats, also known as Pashmina goats, survive in extreme cold at high altitudes, producing some of the softest wool available.
The unique environmental adaptations of these goats result in superior fibers. This natural evolution is what allows pashmina and cashmere to maintain their prestigious reputation.
Together, these goats underpin the exquisite qualities of pashmina and cashmere, each playing a pivotal role in the luxury textile market.
Comparing the Fibers: Pashmina vs Cashmere
The texture and quality of pashmina and cashmere make them standout materials. Despite their similarities, key differences define their individual allure. Understanding these can help you choose the right fabric.
One of the primary distinctions lies in fiber diameter and softness. While both are incredibly soft, pashmina tends to be finer, adding to its luxurious appeal. This fineness contributes greatly to its higher price and rarity.
The warmth and insulation properties are another aspect where these fibers shine. Both are prized for keeping the chill at bay, but they do so with differing levels of efficiency.
When evaluating pashmina and cashmere, consider these elements:
- Fiber diameter and softness
- Insulating capabilities
- Uses and product availability
- Care requirements and longevity
Each of these factors plays a significant role in determining the right choice based on your needs and preferences.
Fiber Diameter and Softness
Fiber diameter is a critical factor in the texture of these luxury fabrics. Cashmere fibers can range from 14 to 19 microns in diameter, which is already quite fine. This fine diameter contributes to its softness, making it comfortable to wear.
Pashmina fibers, however, push the limits even further. They are usually less than 12 microns, giving them an unparalleled softness. This results in a velvety touch that is both exquisite and highly sought after.
The greater fineness of pashmina can result in a slightly different texture. It often feels more delicate, yet still offers the snug feel characteristic of high-quality wool.
Warmth and Insulation
Both pashmina and cashmere are renowned for their superior insulation. Despite their light weight, these fibers provide a significant amount of warmth. This is due to their natural insulating properties, which trap heat efficiently.
Cashmere is already an excellent insulator, making it suitable for cold climates. Its thickness and weave can vary, allowing versatility in different temperatures.
Pashmina offers even greater warmth-to-weight ratio. Its thinner fibers retain warmth exceptionally well, making it ideal for compact, luxurious layers. This makes pashmina a popular choice for travelers seeking comfort without bulk.
The balance of warmth and weight makes both fibers ideal for various climates. They provide comfort without the heaviness often associated with warm fabrics, offering both elegance and practicality.
The Craftsmanship of Pashmina and Cashmere
The artistry involved in producing pashmina and cashmere is a testament to human skill. This craftsmanship combines traditional techniques with contemporary innovations to create stunning products. Each piece is a labor of love, showcasing the precision and care that artisans invest in their craft.
Creating pashmina items requires delicate hand-spinning and weaving. This intricate process results in the luxurious feel and unparalleled quality of pashmina shawls and scarves. The fibers are so delicate that they necessitate gentle handling throughout production to maintain their integrity.
Cashmere craftsmanship often employs a mix of machine and hand techniques. This combination allows for a range of products, from finely woven sweaters to accessories like gloves and hats. These methods enhance the fiber’s natural qualities, emphasizing its soft and warm attributes.
This balance of old and new techniques has helped maintain the cultural heritage of pashmina and cashmere production. In preserving these traditions, artisans ensure that each crafted piece holds a piece of history within its fibers.
Traditional Techniques and Modern Methods
The traditional techniques for creating pashmina have been passed down through generations. Hand-spinning is a meticulous process requiring years of expertise to master. This art form, combined with hand-weaving, gives pashmina its renowned delicacy and charm.
In contrast, cashmere production has embraced modern methods. Advances in textile technology help increase production efficiency while ensuring superior quality. These methods complement hand-finishing techniques, which add an artisanal touch to mass-produced items.
The Artisans and Their Communities
Artisans play a crucial role in preserving the cultural essence of pashmina and cashmere. Their skills are often honed from a young age, ensuring the continuity of traditional craftsmanship. These communities rely heavily on this industry for their livelihood, creating a symbiotic relationship between craft and community.
The production of these luxury items significantly impacts local economies. It not only provides jobs but also fosters cultural pride and identity. Supporting artisan communities through purchasing genuine pashmina and cashmere contributes to sustaining these valuable traditions for future generations.
Care and Maintenance: Ensuring Longevity
Proper care of pashmina and cashmere can significantly extend their lifespan. These luxury fibers, while beautiful, require particular attention. By adopting careful maintenance practices, you can preserve their softness and beauty.
Understanding the nuances of cashmere care is essential. This fiber, renowned for its warmth and delicacy, needs gentle handling. With the right care, cashmere items can last for many years.
Pashmina, being even finer than cashmere, demands an elevated level of care. Its delicate texture can be susceptible to damage if not handled properly. Follow specific tips to maintain the quality of your pashmina.
Here’s a concise care guide for both these precious fibers:
- Hand wash or dry clean only.
- Use mild detergents for washing.
- Lay flat to dry, away from direct sunlight.
- Avoid hanging to prevent stretching.
- Store in a breathable bag to protect from moths.
Developing a good routine for care can keep these fibers looking impeccable. A little care goes a long way in preserving their luxurious appeal.
Cashmere Care Tips
Cashmere requires gentle treatment to maintain its softness. Always choose hand washing with cold water as the safest cleaning method. This minimizes damage from agitation and hot water.
Use a mild detergent specifically designed for delicate fabrics. This helps retain the fiber’s natural oils, which contribute to its softness. Rinse thoroughly to ensure no detergent residue remains.
Avoid wringing out cashmere to prevent distortion. Instead, gently press the water out between towels. Finally, lay the item flat on a dry towel to air dry, reshaping it to its original form.
Pashmina Care Tips
Pashmina care demands attention to detail due to its fine fibers. Opt for dry cleaning when possible, as professionals can handle the delicate fabric. When washing at home, use the gentlest touch in cold water.
Select a baby shampoo or pashmina-friendly detergent. These options are mild and won’t strip the fibers. Ensure complete rinsing to avoid any lingering soap.
For drying, never wring or twist pashmina. Pat out excess water using a towel, then lay flat to dry. This minimizes distortion and keeps the fabric’s integrity intact, safeguarding its exquisite feel.
Identifying Authenticity and Avoiding Counterfeits
As the demand for pashmina and cashmere grows, so does the presence of counterfeits. Identifying genuine products is crucial for making informed purchases. Understanding authenticity indicators is essential to avoid low-quality imitations.
Authentic pashmina and cashmere often come with certifications. These seals of authenticity help consumers recognize genuine articles. Familiarizing yourself with these indicators can save you from costly mistakes.
There are several key signs to look for when identifying real cashmere or pashmina. Recognizing these markers can distinguish high-quality products from fakes.
Consider the following checklist when assessing the authenticity of pashmina or cashmere items:
- Look for a “Chyangra Pashmina” trademark.
- Check for authenticated certifications or labels.
- Pay attention to the fineness and softness of the fabric.
- Ensure a high warmth-to-weight ratio.
- Examine the item’s provenance for origin details.
By keeping these points in mind, you can confidently distinguish between authentic fibers and their imitations.
Certifications and Trademarks
Certifications and trademarks are the first line of defense against counterfeits. Reputable pashmina products often carry the “Chyangra Pashmina” trademark. This certification guarantees the item meets stringent quality standards.
Cashmere also features indicators of authenticity. Look for labels or stamps verifying the fiber’s origin. These marks reassure buyers of the product’s quality and authenticity, helping to confirm their purchase as genuine.
Physical Characteristics and Quality Indicators
The physical characteristics of pashmina and cashmere can also indicate authenticity. Genuine items possess a natural softness that is hard to fake. The fibers should feel warm, light, and free from synthetic shine.
Quality indicators also involve examining the fineness of the fiber. True cashmere and pashmina have an exquisitely soft texture and a subtle sheen. If the fabric feels rough or overly glossy, it may be a blend or counterfeit.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
The production of pashmina and cashmere has significant ecological and ethical implications. Consumers today are more conscious of these issues than ever. As a result, sustainable and ethical production has gained importance in the textile industry.
Increasing demand puts pressure on ecosystems where cashmere goats graze. Overgrazing can lead to land degradation, impacting biodiversity. Ethical sourcing practices aim to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Moreover, ethical considerations extend to the treatment of animals. Ensuring humane practices is critical to ethical cashmere and pashmina production. This consideration aligns with the growing consumer demand for cruelty-free products.
Addressing these challenges requires commitment from producers and consumers alike. Together, they can support practices that prioritize the environment and animal welfare. Such collaboration is essential to sustaining this luxury industry.
Sustainable Practices in Production
Sustainable production practices aim to reduce environmental harm. By managing grazing lands and improving herd management, overgrazing can be minimized. Such efforts help preserve the natural habitats of cashmere and pashmina-producing regions.
Additionally, some producers are exploring alternative methods. These approaches include reducing water use and energy consumption. Embracing innovation in production methods can lessen the environmental footprint of these luxurious fibers.
The Impact of Overgrazing and Climate Change
Overgrazing is a pressing concern in cashmere production. It contributes to soil erosion and desertification, disrupting local ecosystems. This degradation not only affects wildlife but also impacts the local communities reliant on these lands.
Climate change exacerbates these issues. Shifting weather patterns influence the habitats of cashmere-producing goats. Adapting to these changes requires proactive measures by producers and stakeholders. Sustainable practices are vital for the long-term viability of this industry.
| Feature | Pashmina | Cashmere |
| Origin | Derived from Changthangi goats in the Himalayas, particularly Kashmir | Obtained from Cashmere goats, primarily in Mongolia, China, and parts of Central Asia |
| Fiber Diameter | 12-15 microns | 14-19 microns, with finest quality below 14 microns |
| Softness | Extremely soft and fine, often considered softer than Cashmere | Very soft and luxurious |
| Warmth | Excellent insulation despite being lightweight | Provides excellent warmth without bulk |
| Production Process | Traditionally hand-spun and hand-woven | Can be produced using both traditional and modern techniques |
| Durability | Traditionally hand-spun and hand-woven | Long-lasting with proper care |
| Cultural Significance | High cultural value in Kashmir, symbolizing prestige and heritage | Widely recognized globally as a luxury fiber |
| Typical Products | Shawls, scarves, and fine garments | Sweaters, scarves, coats, and accessories |
| Market Size (2023) | Global Pashmina shawls market valued at $144.78 million | Global Cashmere clothing market valued at $2.7 billion |
| Market Growth | Projected CAGR of 6.47% (2023-2031) | Projected CAGR of 5.4% (2023-2030) |
| Primary Production Regions | Ladakh region in India | Mongolia, China, and Iran |
| Production Scale | Largely artisanal, small-scale workshops | More industrialized, capable of large-scale production |
| Sourcing Challenges | Limited by availability of raw materials and skilled artisans | Affected by climate change and overgrazing in source regions |
| Quality Grading | Not typically graded, known for overall fineness | Graded (A, B, C) based on fiber diameter |
| Blending | Often blended with silk to enhance texture and sheen | Typically used pure, but sometimes blended for specific products |
| Certification | May be certified by local authorities in Kashmir | Often certified by international bodies like IWTO or Woolmark |
| Sustainability Concerns | Concerns about authenticity and ethical sourcing | Growing focus on sustainable and ethical production practices |
| Care Requirements | Requires gentle care, often dry clean only | Requires careful washing and storage to maintain quality |
| Price Point | Generally higher due to rarity and labor-intensive production | Expensive, but more widely available than Pashmina |
Conclusion: Making an Informed Choice
Choosing between pashmina and cashmere depends on personal preferences and values. Understanding their differences allows consumers to make better-informed decisions for their purchases and lifestyle.
Summary of Key Takeaways
Pashmina and cashmere are renowned for their softness and warmth. Originating from different goats, they offer unique qualities. Pashmina, often finer and more delicate, tends to be more expensive due to its rarity. Meanwhile, cashmere offers a broader range of products. Both materials require careful handling and ethical sourcing considerations. Recognizing authentic products is crucial in a market filled with imitations.
The Future of Luxury Textiles
The future of luxury textiles hinges on sustainable and ethical practices. As consumer awareness grows, so will the demand for transparency and environmental responsibility in the industry. Embracing these changes will ensure the resilience and prestige of pashmina and cashmere.

 French
French  Deutsch
Deutsch  Spanish
Spanish  الإمارات
الإمارات  English
English 

